Microsoft Exam #70-215: Installing, Configuring, and Administering Windows 2000 Server
6 questions. Answers can be found at the end of the quiz.
courtesy of Transcender LLC
Questions
1. A Windows 2000 file server hosts home directories of several hundred users. Files are intensively written and deleted on the computer's disks, which causes fragmentation. You do not want to perform the defragmentation prematurely. Which of the following commands should you use to determine whether you should run the defragmentation utility on a particular disk?
a. Defragment in Disk Defragmenter
b. Check Now on the Tools tab in the disk's Properties page
c. Analyze in Disk Defragmenter
d. Defragment Now on the Tools tab in the disk's Properties page
2. Your corporate network includes 230 Windows 2000 computers and 18 UNIX computers. There is a print device attached to a UNIX computer, and you want to enable Windows 2000 clients to print to that device. You want to accomplish this task in the most efficient and economical manner. Which of the following steps should you take?
a. Install Print Services for UNIX on a Windows 2000 Server print server.
b. Install an LPR port on each Windows 2000 client computer.
c. Install an LPR port on the Windows 2000 Server print server.
d. Install Print Services for UNIX on the UNIX print server.
e. Install an LPR port on the UNIX print server.
f. Install Print Services for UNIX on each Windows 2000 client computer.
3.You are a Windows 2000 network administrator for your company. All computers in the Marketing department belong to the Marketing organizational unit (OU). You suspect that someone has been trying to gain unauthorized access to files on the computers in Marketing. You want to identify that person without affecting other computers. Which two steps should you take to accomplish this task with the least amount of administrative effort?
a. Enable an audit policy for the Marketing OU.
b. Enable auditing for the Everyone group for the files or folders that you suspect are under attack.
c. Enable an audit policy for each computer in the Marketing OU individually.
d. Enable auditing for the Marketing group.
4. You have implemented a Windows 2000 Server computer on your company's network and configured it as a file server. Windows NT and Windows 98 users complain that they cannot connect to the new server to store their files on it. TCP/IP is configured on the file server as shown in the exhibit.
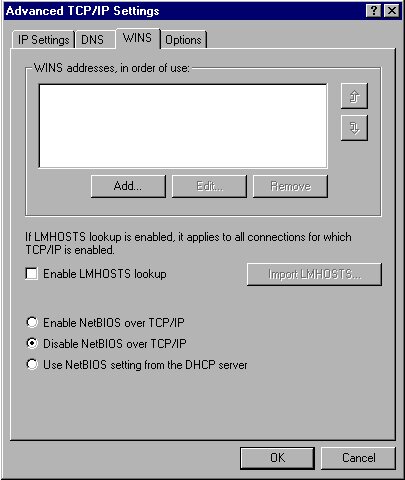
What changes should you make in the configuration of the file server to correct the problem?
a. Specify the IP address of at least one WINS server.
b. Enable LMHOSTS lookup.
c. Enable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
d. Import the same LMHOSTS file that the Windows NT and Windows 98 clients are using.
5. A user named Susan needs to encrypt her files that are stored on several Windows 2000 file servers. Because of the sensitive nature of her work, Susan is allowed to interactively log on to each of the file servers and to access her files locally. She is not allowed remote access to these files. After the files have been encrypted, she should be able to edit the files and then save the edited versions with the encryption in place. Which of the following should you do to provide Susan with the required functionality?
a. Nothing needs to be done. Susan can encrypt and decrypt any file that she owns on any file server to which she has access.
b. Enable the file servers to be trusted for delegation.
c. Create a roaming user profile for Susan.
d. Implement a certification authority (CA).
6. Andrew is a new employee who has been designated as an administrator of your corporate network, which includes several Windows 2000 domains. Working interactively on a Windows 2000 member server, Andrew attempts to run Windows Update in order to install several critical updates. Andrew receives an error message that indicates that he does not have the necessary permissions to install the updates. Which of the following actions is most likely to enable Andrew to install the updates?
a. Andrew should log on as a member of the Enterprise Admins universal group.
b. Andrew should log on as a member of the Domain Admins global group in the domain where the member server belongs.
c. Andrew should log on as a member of the built-in Administrators local group on the member server.
d. Andrew should log on as a member of the built-in Administrators local group in the domain where the member server belongs.
Answers:
1) Choice c is correct. To determine whether you should run defragmentation without actually starting the defragmentation process, you should click Analyze in Disk Defragmenter. The physical structure of the files on a specific volume will be analyzed, and you will receive a color diagram and a tabular report. Using this information, you can decide whether you should actually defragment that volume. The Defragment command in Disk Defragmenter also performs the same analysis, but you do not receive a tabular report; instead, defragmentation starts immediately. The Check Now button on the Tools tab in the volume's Properties page is used to start the program that checks and can automatically correct certain types of data integrity problems. Clicking the Defragment Now button on the Tools tab in the volume's Properties page only causes the Disk Defragmenter window to appear; neither analysis nor defragmentation will start until you click the appropriate button in Disk Defragmenter. Reference: W2KSOH, Contents, "Monitoring and Diagnostics Tools," "Disk Defragmenter," "Concepts," "Disk Defragmenter overview." W2KSOH, Contents, "Monitoring and Diagnostics Tools," "Disk Defragmenter," "Concepts," "Understanding Disk Defragmenter (entire section)." W2KSOH, Contents, "Monitoring and Diagnostics Tools," "Disk Defragmenter," "How To... (entire section)."
2) Only choices a and c are correct. The best way to enable Windows 2000 users to print to the print device on a UNIX print server is to install a printer for that print device on a Windows 2000 Server print server and then share the printer. On the Windows 2000 Server print server, you should install Print Services for UNIX, install an LPR-compliant port, install the appropriate printer on the LPR port, and then share the printer. The LPR port on a Windows 2000 computer implements a print client for the LPD utility, which is the native UNIX print server utility. Windows 2000 clients will not need any additional software to connect to the printer shared on the Windows 2000 print server. The driver will be downloaded and installed automatically on a Windows 2000 client computer the first time that the client connects to the shared printer. Alternatively, you can install Windows Services for UNIX on each Windows 2000 client computer, install an LPR port and install the printer. However, this is not the best solution because it requires more effort to install the printer on all Windows 2000 client computers than to install it only once on a Windows 2000 Server print server. Print Services for UNIX and an LPR port are Windows 2000 components; they cannot be installed on UNIX computers. UNIX print servers run the native LPD utility, and UNIX print clients run the native LPR utility. Reference: W2KSRK, Contents, "Server Operations Guide," "Storage, File Systems, and Printing," "Network Printing," "Working with Other Operating Systems," "Printing with UNIX Clients and Servers Using LPR/LPD."
3) Choices a and b are correct. To track access attempts to file resources on computers in the Marketing OU, you should first create a Group Policy object linked to the OU. Open the policy in Group Policy Editor and navigate to the node Computer Configuration/Windows Settings/Security Settings/Local Policies/Audit Policy. In the right pane, click Audit object access, select Security from the Action menu and enable auditing of success and failure. Then, you should use Windows Explorer to configure auditing for particular files or folders on the appropriate computers. Instead of creating a Group Policy object for the OU, you can enable an audit policy locally on each computer. However, this would require more effort than configuring a single policy one time. If you audit access only by users who belong to the Marketing group, then you may miss the perpetrator because he or she may be anyone, not necessarily a member of the Marketing group. Reference: W2KSRK, Contents, "Deployment Planning Guide," "Active Directory Infrastructure," "Planning Distributed Security," "Setting Uniform Security Policies," "Group Policy." W2KSRK, Contents, "Deployment Planning Guide," "Active Directory Infrastructure," "Planning Distributed Security," "Setting Uniform Security Policies," "Group Policy Security Settings." W2KSOH, Contents, "Security," "Concepts," "Understanding Security," "Auditing Security Events (entire section)." W2KSOH, Contents, "Security," "How To...," "Audit Events (entire section)."
4) Choice c is correct. NetBIOS is a naming convention and a programming interface that was used with previous versions of Windows, such as Windows NT, Windows 9x and Windows 3.x. Computers with these operating systems used a flat NetBIOS namespace and identified each other by NetBIOS names. On routed networks, either WINS, server-based name resolution service, or a local LMHOSTS file on each computer had to be used for mapping computer names to their IP addresses. Additionally, NetBIOS was also used to provide support for browsing in Network Neighborhood. Windows 2000 uses DNS naming service and does not require NetBIOS in a purely Windows 2000 environment. However, Windows 2000 supports both NetBIOS and WINS for backward compatibility with earlier versions of Windows in a mixed environment. In this scenario, you should enable NetBIOS over TCP/IP on the new Windows 2000 file server, and then the users of down-level Windows computers will be able to locate the file server and to store their files on it. You can specify the IP address of a WINS server or enable LMHOSTS lookup and create or import an LMHOSTS file. However, none of those steps is necessarily required. If the network is not routed, then all computers can use broadcasts for NetBIOS name registration and resolution. Even if the network is routed, only the client computers would need to use NetBIOS name resolution means, such as WINS or LMHOSTS files, because client computers initiate all connections for file access. The server responds to a client request by using the client's IP address provided in the request. Reference: W2KSRK, Contents, "Deployment Planning Guide," "Active Directory Infrastructure," "Determining Domain Migration Strategies," "Planning Domain Upgrade," "Using NetBIOS with Windows 2000." W2KSRK, Contents, "TCP/IP Core Networking Guide," "Windows 2000 TCP/IP," "Windows 2000 TCP/IP," "Network Application Interfaces," "NetBIOS over TCP/IP."
5) Choice a is correct. Encrypting File System (EFS) generates a unique file encryption key for each file that is encrypted. After the file has been encrypted, the file encryption key is encrypted with the user's public key. To decrypt the file, EFS must first decrypt the file encryption key by using the user's private key. Both the public and private keys are associated with the user's certificate, which can be issued either by a CA or by EFS if no CA is available. The certificate and the keys are stored in the user's profile. When Susan interactively logs on to a file server for the first time, her local user profile is created on that computer. The first time she encrypts a file on that computer, a copy of her certificate will be installed in her local profile. Therefore, she can log on interactively to her domain user account from any of the file servers and encrypt and decrypt any of her files on those computers. If Susan had to encrypt and decrypt files on a remote file server while she is logged on to her workstation, then the remote server would have to be trusted for delegation in order to be able to access Susan's certificate and the associated keys in her local user profile on her workstation. A roaming user profile is a profile that is stored somewhere on a network share and is loaded whenever the user logs on to his or her domain account from different computers. The path to a roaming user profile is specified in the user's account properties. If Susan were assigned to several workstations in the company from which she had to encrypt and decrypt her files on a remote file server, then the remote file server would have to be trusted for delegation and Susan would have to use a roaming user profile. In that case, her certificate would be downloaded together with the profile to the workstation that she would be using, and then the certificate would be destroyed when she logged off or when the computer was restarted. Reference: W2KSRK, Contents, "Distributed Systems Guide," "Distributed Security," "Encrypting File System," "Introduction to EFS," "Features of EFS." W2KSRK, Contents, "Distributed Systems Guide," "Distributed Security," "Encrypting File System," "Introduction to EFS," "What the User Sees." W2KSRK, Contents, "Distributed Systems Guide," "Distributed Security," "Encrypting File System," "Introduction to EFS," "How EFS Works." W2KSRK, Contents, "Distributed Systems Guide," "Distributed Security," "Encrypting File System," "Introduction to EFS," "How Certificates Are Stored."
6) Choice c is correct. Andrew is unable to install the updates because the user account with which he logged on has insufficient permissions on the member server. The most powerful group on the member server is the built-in Administrators local group that is defined on that computer. If Andrew can log on as a member of the built-in Administrators local group on the member server, then he will most definitely have all of the permissions that may be necessary to install the updates. By default, the Domain Admins global group is made a member of the built-in Administrators local group on each member server in the domain. However, Domain Admins can be removed from the built-in Administrators local group on any of the member servers in that domain. Therefore, logging on as a member of Domain Admins is less likely to provide Andrew with the necessary permissions. Enterprise Admins is a universal group that resides in the forest's root domain and, by default, is a member of the built-in Adminstrators local group in each domain in the forest. However, membership in the built-in Administrators local group in the domain does not provide any administrative privileges on member servers. Reference: W2KSRK, Contents, "Server Operations Guide," "Troubleshooting," "Troubleshooting Strategies," "Troubleshooting Tools for Windows 2000," "Windows Update." W2KSRK, Contents, "Distributed Systems Guide," "Appendixes," "Well-Known Security Identifiers."
These questions and answers are provided by Transcender LLC. Order the full version of this exam simulation online at www.transcender.com, phone 615-726-8779, 8 a.m. - 6 p.m., (CST), M - F, fax 615-726-8884, or mail to Transcender LLC, 565 Marriott Drive, Suite 300, Nashville, TN 37214.
More Pop Quiz:
|


