|
5/18/2007 -- I recently discussed on my blog a major problem with starting Internet Explorer 7 in Windows Vista. Usually, I use Mozilla Firefox as my default browser, and take advantage of its Internet Explorer Extension Tab so I can avoid using IE for Web sites that require it. However, sometimes I have no choice but to use Internet Explorer.
But one day, IE7 failed to start while I was logged in as an account that had administrative privileges. Instead of getting my home page, which was set to http://www.seattlepro.com/, I got the "File Download - Security Warning" message whenever I tried to start the browser. The warning message asked me if I wanted to save the file seattlepro.com. Regardless of what action I took, Save or Cancel, Internet Explorer failed to start.
I tried to start IE without add-ons by going to Start, All Programs, Accessories, System Tools, Internet Explorer (no add-ons), but that didn't help. When I set my default page to "blank," I got a similar error (see Figure 1).
Name: navcancl
Type: Unknown File Type, 2.64KB
From: ieframe.dll

[Click on image for larger view.] |
| Figure 1. File Download - Security Warning in Internet Explorer 7. |
When I started IE as an administrator by right-clicking IE and selecting Run as Administrator, IE started fine. In Windows Vista, even if you are logged in as an administrator account, IE runs with limited privileges by default (this is one of the security features in Windows Vista that's meant to keep your computer safe). Obviously, I didn't want to configure IE to run as Administrator automatically and was looking for a better solution.
After some troubleshooting, I realized that somehow the Protected Mode was turned on for the Trusted sites zone. I turned it off only for the Trusted sites zone and left it enabled for the rest of the zones, and that allowed me to start my browser normally. I was able to go to some of the sites but not all; I was only able to go to the Web sites that were in my Trusted sites list.
(Note that in earlier versions of Windows, you can remove IE7 completely from your operating system. However, in Vista, IE is part of the operating system and cannot be removed.)
While surfing Microsoft newsgroups, I found out that I was not the only one experiencing this problem. A lot of people were having different kinds of problems, and they're not limited to Vista users, either. The problem also appeared on Windows XP SP2 and Windows Server 2003 computers running IE7. Several users, including Microsoft MVPs, reported that the problem was caused by the May 2007 Cumulative Security Update for IE (MS07-027). Microsoft later confirmed that this was the cause and posted a Knowledge Base article that offered a workaround.
According to Microsoft, the problem with IE occurs if:
- The Temporary Internet Files folder is moved to a location outside the Users folder hierarchy
- The Phishing Filter is enabled
- The Protected Mode is enabled
However, these conditions aren't always applicable. For example, I know people who have experienced this problem even when they have the Phishing Filter disabled.
Microsoft's offers two possible workarounds:
- Move the Temporary Internet Files back to its original location
- Configure permissions for Temporary Internet Files folder
If you move the Temporary Internet Files folder back to the original location, the user account has Full Control permissions to the folder hierarchy and everything works normally.
If you decide to use the second workaround, which requires modifying the permissions, then you will have to update NTFS permissions for the folder that's above the Temporary Internet Files folder. For example, if you moved your Temporary Internet Files folder to the root of drive C, then you would have to give the user who can't start IE Full Control permission at the root of drive C because that is the folder that is above the Temporary Internet Files folder.
This may not be a good idea. For security reasons, a better option will be to move the Temporary Internet Files back to its original location within the user's profile while Microsoft investigates a possible solution for this issue.
Remember that what KB article 937409 offers is only a temporary workaround; it doesn't fix the problem caused by the cumulative security update. Microsoft says that it's aware of the problems caused by this update and is working to fix it.
Here's the procedure for modifying permissions on Windows Vista computers. Before implementing this procedure, make sure you understand the consequences, especially if your Temporary Internet Files folder is located in the root of your drive.
- Go to Control Panel, Network and Internet, Internet Options.
- On the General tab, click Settings in the Browsing History area.
- Click View Files.
- In the Windows Explorer address box, click the folder name that comes before Temporary Internet Files.
- Right-click the folder and then click Properties.
- On the Security tab, click Edit.
- If prompted, click Continue at the UAC prompt.
- Click the name of the affected user. If the name is not listed, add the user's name.
- Give the user Full Control permission.
- Click Apply, and then click OK.
- Close all windows and restart IE.
After restarting IE, you should be able to work in the browser normally.
This procedure applies to Windows Vista computers. For modifying permissions on Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 computers, check out KB article 937409.
Have you experienced any issues with the May 2007 Cumulative Security Update for IE that you would like to share with readers? Let me know at or leave a comment below.
|

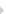 Column Story
Column Story

