CompTIA Exam: Server+
7 questions. Answers can be found at the end of the exam.
courtesy of Transcender LLC
Questions
1. You want to flash the basic input/output system (BIOS) of a server. You back up the server's hard disk and document the server's complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) settings. You also create a bootable floppy disk that contains the files necessary to perform the flash update. Which of the following steps should you take next?
a. Run the flash utility.
b. Back up the current BIOS.
c. Reboot the server from the floppy disk.
d. Reboot the server without the floppy disk.
2. You administer a server that contains a Pentium III Coppermine central processing unit (CPU) that is rated at a speed of 750 megahertz (MHz) and has a 256-kilobyte (KB) level 2 (L2) cache. You want to install an additional CPU in the server. Which of the following criteria should the additional CPU meet?
a. The additional CPU should be rated at a speed of 750 MHz or less.
b. The speed of the additional CPU should be the fastest available at the time of the installation.
c. The additional CPU should have a 256-KB L2 cache.
d. The additional CPU should be assigned a higher stepping level than the original CPU.
3. You administer a network that includes 150 client computers, a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, a Domain Name System (DNS) server, 2 file servers, 3 print servers, and a firewall. You want to configure hosts that provide network-critical functions with static Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. You do not plan to create any DHCP reservations. Which of the following hosts should receive their IP addresses from the DHCP server?
a. the client computers
b. the DHCP server
c. the DNS server
d. the file servers
e. the print servers
f. the firewall
4. You are the chief network administrator for a mid-sized corporation that has several offices located throughout the Southeast. Because of a recent hurricane in Miami, the city where your company's headquarters is located, several years' worth of financial data on multiple database servers has been permanently lost. Which of the following actions could you have taken to protect the data?
a. Store copies of backups at the headquarters.
b. Store copies of backups at a separate location in Miami.
c. Store copies of backups at a branch office in another state.
d. Maintain a hot site at the headquarters.
5. You administer several servers in a server room. All the computer equipment in the server room is mounted in server racks. You want to provide physical security for the servers in the server room. Which of the following is the least effective method you can use to accomplish this task?
a. Require users to specify a user name and password to gain access to files on the servers.
b. Install a key card reader on the server room door.
c. Lock the server racks.
d. Install surveillance cameras in the server room.
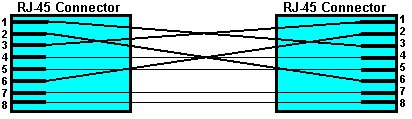
6. You administer a server on an Ethernet network, and you encounter the cable in the following exhibit: How should you use this cable?
a. to connect the server to a MAU
b. to connect the server to a hub
c. to connect the server to another server
d. to connect the server to a JABODS
7. You are a corporate network administrator. A new numeric keypad has been installed to control access to the server room. You must decide which individuals should be notified of the combination required to enter the server room. You are considering giving the combination to the following personnel: I. the housekeeping staff II. the IT staff III. users of client computers IV. your assistant network administrator To which personnel should you provide the combination?
a. I and II, only
b. II and IV, only
c. I, II and III, only
d. II, III and IV, only
Answers
1) Answer: c. Your next step should be to reboot the server from the floppy disk. Before flashing a computer's BIOS, you should always back up the server's hard disk in case problems occur after the BIOS update. You should also document the CMOS settings because you may have to reset them after the update. The flash update can be downloaded from the Web site of either the BIOS manufacturer or the system board manufacturer. You should create a bootable floppy disk for the operating system that is supported by the flash BIOS utility, and you should place the flash update files on the floppy disk. No other files should be placed on the floppy disk. You should then attempt to reboot the server from the floppy disk. By booting the server from the floppy disk, you ensure that only the necessary software is running during the flash process. Unnecessary software and drivers can interfere with the flash process and cause it to fail. If the server is configured to look first for an operating system on a hard disk during the startup process, then you should enter the CMOS setup and configure the server to look first for an operating system on a floppy disk. Otherwise, you will not be able to start the server from the floppy disk you created because the server will not look for an operating system on the floppy disk. After the boot process completes, run the flash utility from the floppy disk and specify any information that the utility requests. Choose to back up the BIOS if the flash utility prompts you to do so. Next, run the flash utility to install the BIOS update. You must be careful not to interrupt the update process or shut down the computer before the update is completed, because doing so may leave the computer in an unusable state. Once the flash update completes, manually turn off the server, remove the floppy disk, restart the server and, if necessary, reset the CMOS settings that you recorded before you performed the update. Reference: TMRP, Chapter 7, Flashing The BIOS, pp. 189-190. SSGe, Bookmarks, "Chapter 8: Inside the Server Room," "Updating Firmware," "Applying Firmware Updates."
2) Answer: c. When multiple processors are installed in the same computer, they should each have the same speed and the same L2 cache size. Thus, the additional CPU should also run at a speed of 750 MHz; using a processor that is rated slower than or faster than 750 MHz will likely cause the server to perform erratically or malfunction. If the original CPU is obsolete, then you may need to replace that CPU with two new CPUs that comply with the processor criteria set forth by the server's manufacturer. The additional CPU should not be the fastest CPU available unless the server supports that speed and you also replace the original CPU with one that matches the additional CPU. As improvements are made to a particular processor model, the resulting processors are assigned higher stepping values. Stepping values indicate the version of a particular processor model. If possible, the additional CPU should be assigned the same stepping level as the original CPU. If you cannot obtain an additional CPU that has the same stepping level as the original CPU, then you should ensure that the stepping level of the new CPU is within a range that the server manufacturer indicates is compatible with the original CPU. Reference: TMRP, Chapter 1, CPU Upgrade Potential, pp. 6-7. SSGe, Bookmarks, "Chapter 3: CPUs and Fibre Channel," "Adding Processors."
3) Answer: a. Only the client computers should receive their IP addresses from the DHCP server. DHCP servers are used to dynamically assign IP addresses to network devices. To ensure that client computers can always locate hosts that provide network-critical functions, hosts such as DHCP servers, DNS servers, file servers, print servers, routers and firewalls should be configured with static IP addresses. IP addresses for DHCP servers should always be manually configured. DHCP reservations can be used to ensure that certain hosts, such as the remaining servers in this scenario, always receive the same IP address. However, because you do not plan to create any DHCP reservations in this scenario, you should manually configure the IP information for hosts that require static IP addresses. Reference: www.microsoft.com/technet/treeview/default.asp?url=/TechNet/prodtechnol/windows2000serv/reskit/tcpip/part2/tcpch04.asp TechNet, Contents, "MS Product Family," "MS Windows 2000," "MS Windows 2000 Server," "Resource Kit," "Windows 2000 Server TCP/IP Core Networking Guide," "Part 2 - Address Allocation and Name Resolution," "Chapter 4 - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol."
4) Answer: c. One approach to protecting corporate data, which is often more valuable than the equipment on which it is stored, is to keep copies of data backups at a remote location that is unlikely to be affected by the same natural disaster as the primary location. Because the company in this scenario has several offices located throughout the Southeast, it is advisable to store copies of data backups at a remote branch office outside the state of Florida to decrease the possibility that a hurricane will destroy all copies of the data. Although you can also choose to store backups locally or at a separate, nearby location, such backups are more likely to be destroyed by the same natural disaster. Hot site technology involves a failover cluster or a true cluster in which additional servers that run identical services and store identical data almost seamlessly assume the functionality of primary servers in the event of failure. A local hot site can protect against hardware failure, but it cannot protect against natural disaster because the failover cluster is likely to be destroyed along with the active servers. Reference: NSG, Chapter 10, Assessing Fault Tolerance and Disaster Recovery Needs, pp. 412-417.
5) Answer: a. Of the choices listed, requiring users to specify a user name and password to gain access to files on the servers is the least effective method you can use to provide physical security for the servers in the server room. You generally implement physical security measures to protect equipment from theft. Requiring a user name and password helps protect the data on the servers from theft but does not protect the computer equipment from theft. Installing a key card reader on the server room door is an effective physical security measure because only individuals with a valid key card can enter the server room. Locking the server racks is also an effective physical security measure because servers in locked racks are generally harder to steal than servers in unlocked racks. Finally, installing surveillance cameras in the server room is an effective physical security measure because security cameras can enable you to record and identify individuals who steal or attempt to steal equipment from the server room. Reference: SSGe, Bookmarks, "Chapter 7: Server Etiquette," "Physical Server Security." SSGe, Bookmarks, "Chapter 8: Inside the Server Room," "Recognizing and Reporting on Physical Security Issues." SCTKe, Contents, "Chapter 2 -- Planning a Server's Environment," "Lesson 1: Space Planning."
6) Answer: c. You should use the cable depicted in the exhibit to connect the server's network interface card (NIC) to a NIC in another server. The cable depicted in the exhibit is a crossover Ethernet cable. In an RJ-45 Ethernet connector, pins 1 and 2 are used to transmit data and pins 3 and 6 are used to receive data. In a crossover Ethernet cable, pins 1 and 3 are connected and pins 2 and 6 are connected, which enables two computers to transmit data to one another without an intervening hub. You can also enable two Ethernet hubs to communicate by connecting them with a crossover Ethernet cable. You can use a standard Ethernet cable, which is sometimes referred to as a straight Ethernet cable, to connect a computer's NIC to a hub. The following exhibit depicts the wiring configuration of a standard Ethernet cable and a crossover Ethernet cable.
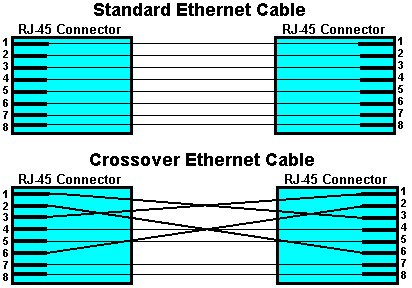 A Multistation Access Unit (MAU) is used on a Token Ring network to concentrate network connections. In this scenario, the server is on an Ethernet network, so you should not use the cable depicted in the exhibit to connect the server to a MAU. A just a bunch of disks (JABODS) is a case that contains hard disks used in a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) array. Generally, you connect a JABODS to a RAID controller by using a Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) cable, such as a high-density 68-pin SCSI cable. You should not use a standard or crossover Ethernet cable to connect a JABODS to the server. Reference: NSG, Chapter 11, The Crossover Cable, pp. 510-511.
7) Answer: b. Only personnel who are involved in network administration should be allowed to enter the server room. Therefore, you should give the combination to only your assistant network administrator and the other members of the IT staff. Allowing entrance to personnel who are not involved in network administration exposes the servers to the possibility of theft and damage, and increases the likelihood of unauthorized access to data. The housekeeping staff could inadvertently disconnect cables, and users could push buttons and flip switches out of curiosity. Thus, it is best to limit server room access to experienced computer personnel. Reference: SSGe, Bookmarks, "Chapter 7: Server Etiquette," "Physical Server Security." SSGe, Bookmarks, "Chapter 8: Inside the Server Room," "Recognizing and Reporting on Physical Security Issues."
These questions and answers are provided by Transcender LLC. Order the full version of this exam simulation online at www.transcender.com, phone 615-726-8779, 8 a.m. - 6 p.m., (CST), M - F, fax 615-726-8884, or mail to Transcender LLC, 565 Marriott Drive, Suite 300, Nashville, TN 37214.
More Pop Quiz:
|

 Pop Quiz Article
Pop Quiz Article