CompTIA Exam: Network+
6 questions. Answers can be found at the end of the quiz.
courtesy of Transcender LLC
Questions
1. How should you use the Ping utility to determine whether the NIC in your local computer is functioning properly? (Select all choices that are correct.)
a. You should ping the local loopback address.
b. You should ping your local Internet Protocol (IP) address.
c. You should ping a node on your network.
d. You should ping a node on a remote network.
2. Which layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model supports server message blocks (SMBs)? (Select the best choice.)
a. the Physical layer
b. the Network layer
c. the Session layer
d. the Application layer
3. Which technologies can use time division multiplexing (TDM)? (Select all choices that are correct.)
a. baseband
b. broadband
c. Ethernet
d. Fast Ethernet
e. IDE
4. Which protocol allows hosts on a TCP/IP network to communicate using either parallel or serial connections? (Select the best choice.)
a. DHCP
b. PPP
c. SLIP
d. TCP
5. Which of the following statements describe share-level security? (Select all choices that are correct.)
a. Each user has a user name.
b. Each user has a password.
c. Each resource has a password.
d. It is used on a peer-to-peer network.
6. Which of the following devices are used to connect the computers to the network in the graphic, below? (Select the best choice.)
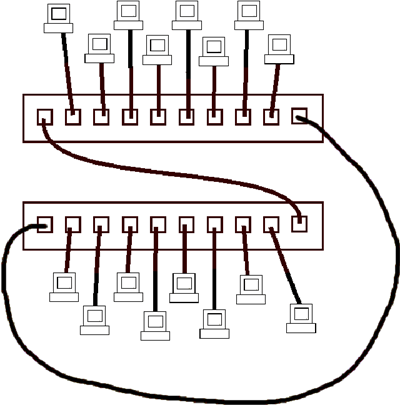
a. MAUs
b. hubs
c. routers
d. default gateways
Answers:
1) Only choices b, c and d are correct. You should use the Ping utility to ping the IP address of your local computer, a node on your network or a node on a remote network to determine whether the computer's NIC is functioning properly. If these troubleshooting steps do not work, then you can try either reinstalling TCP/IP or installing a new NIC in the computer. If you use the Ping utility to ping the local loopback address of 127.0.0.1, then you can determine whether the TCP/IP stack is properly configured on the local computer. Reference: NCSG, Chapter 5, Troubleshooting with TCP/IP Utilities, pp. 210-214.
2) Choice d is correct. The Application layer of the OSI model supports SMBs. Microsoft network redirectors use the SMB protocol to direct data either to the local computer or to the network. The NetWare Core Protocol (NCP), which is used in Novell redirectors, also resides at the Application layer of the OSI model. The Application layer of the OSI model controls the use of the network. The Physical layer of OSI model defines network interface card (NIC) specifications and cable specifications. This layer is responsible for sending data over the physical medium. The Network layer of the OSI model is responsible for routing, addressing and managing network traffic. The Session layer of the OSI model synchronizes computers that are communicating over the network and allows two computers that are linked to a network to establish a session, or communication channel. Reference: NCSG, Chapter 1, SMB and Novell NCP, pp. 28-29.
3) Only choices a, b, c and d are correct. Baseband technologies can use time division multiplexing (TDM) to transmit data signals more efficiently. In TDM, signals are allowed to use the network medium for a certain block of time. When this block of time has expired, then the signal must give up the network medium to another signal. Blocks of time are rotated from one signal to the next in round-robin fashion. TDM can also be used with frequency division multiplexing (FDM) in broadband communications to further divide the separate bandwidth regions into blocks of time. Ethernet and Fast Ethernet are baseband communications technologies. An Ethernet network normally transmits at 10 megabits per second (Mbps). A Fast Ethernet network normally transmits at 100 Mbps. Broadband communications technology uses FDM. A broadband technology uses only a portion of the bandwidth of the network medium. A baseband technology uses all of the bandwidth that is available on the network medium. FDM is the process of dividing a cable into separate bandwidth regions and then sending data signals through the individual bandwidths. Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) is a hard disk technology that cannot use TDM. Reference: NSG, Chapter 1, Signaling Methods, p. 25; NSG, Chapter 2, Physical Layer Concepts, pp. 43-44.
4) Choice b is correct. Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) allows hosts to communicate by using TCP/IP over serial or parallel links. PPP is easy to configure because, when a PPP client connects to a router, the router uses the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign the client computer an Internet Protocol (IP) address, a subnet mask and a default gateway. PPP is more processor-intensive than its predecessor, Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP). As the name suggests, SLIP is capable of serial communications only. TCP/IP communications can be either connection-oriented or connectionless. Connection-oriented communications, which guarantee packet delivery, are performed by Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). User Datagram Protocol (UDP) provides connectionless communications, which are faster but are not guaranteed to transmit successfully. Reference: NSG, Chapter 6, Remote Access Protocols, pp. 266-270; NSG, Chapter 2, The TCP/IP Protocol, p. 70; NSG, Chapter 4, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, p. 156.
5) Only choices c and d are correct. Share-level security is implemented by assigning each resource a password on a peer-to-peer network. This type of security is suitable for a network that has a few resources and a small number of trustworthy and somewhat computer-savvy users. In other words, share-level security relies on the abilities, discipline and honesty of the network users. Users are expected to remember the passwords to each resource, but they are also expected to refrain from sharing passwords with users who do not need access to particular resources. Users preferably should not keep a written list of passwords, or if they do, then they should keep the list in a secure place. Thus, share-level security has many potential pitfalls that make it inappropriate for all large networks and perhaps most small ones. User names and user passwords are characteristics of client/server networks that have implemented user-level security. Users need only remember one password. Access to resources is the responsibility of the network administrator, not the individual users. The network administrator implements resource access through the configuration of Access Control Lists (ACLs). Reference: NSG, Chapter 9, Network Resource Sharing Security Models, pp. 362-363.
6) Choice a is correct. In the graphic, Multistation Access Units (MAUs) are used to connect the computers to the network. Token Ring networks use MAUs to connect computers in a physical star topology, and the MAUs route data packets through the network in a logical ring topology. You can determine that these devices are MAUs because the ring-in port of one MAU is connected to the ring-out port of the other MAU. Hubs are used to connect some Ethernet networks, such as a 10BaseT Ethernet, in a physical star topology. The hub then broadcasts data in a logical bus. Routers and default gateways are computers that route data on a network. A router sends packets from one network to another. A default gateway is a router that computers use if they cannot find the node that they are attempting to contact on the local network and they do not know the address of the router to use to contact the receiving computer's network. Reference: NSG, Chapter 2, The Multistation Access Unit (MAU), pp. 49-50.
These questions and answers are provided by Transcender Corporation. Order the full version of this exam simulation online at www.transcender.com, phone 615-726-8779, 8 a.m. - 6 p.m., (CST), M - F, fax 615-726-8884, or mail to Transcender LLC, 565 Marriott Drive, Suite 300, Nashville, TN 37214.
More Pop Quiz:
|

 Pop Quiz Article
Pop Quiz Article
