|
From CertCities.com
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PopQuiz Microsoft Exam 70-216: Implementing and Administering a Windows 2000 Network Infrastructure 6 questions. Answers and explanations can be found at the end of the quiz. courtesy of Transcender LLC Questions: 1. You administer a small Windows 2000 network that includes 2 Windows 2000 Server computers and 40 Windows 2000 Professional computers. All computers on the network have statically configured IP addresses. You have installed IIS on one of the Windows 2000 Server computers, and you want the computer to host your company's Web site. You have installed Routing and Remote Access and the Network Address Translation (NAT) protocol on the other Windows 2000 Server computer, and you want all Internet hosts to access your Web site through the NAT server. You have established a physical connection between the NAT server and your ISP, and you have created a private interface and a public interface for the NAT protocol. You have statically configured a valid internal IP address for the private interface of the NAT server, and you have statically configured a single ISP-assigned IP address for the public interface of the NAT server. Which of the following actions should you take to enable Internet hosts to access your Web site?
2. The corporate headquarters of Metroil Corporation is in Akron, Ohio. Metroil has branch offices in Bloomington, Illinois; Nashville, Tennessee; Russellville, Arkansas; and Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. Metroil plans to deploy a Windows 2000 network, and you are responsible for the Domain Name System (DNS) structure. You want to allow each office to fully manage its own DNS database and have the ability to create subdomains of their own namespace. Additionally, you want to minimize costs related to the DNS system, but not at the expense of the other goals. Which of the following should you do to meet these goals?
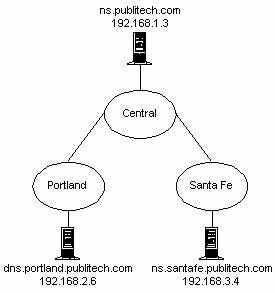
3. You administer a Windows 2000 network for the North American branch of a company named PubliTech. PubliTech's domain name is publitech.com. A DNS server named ns.publitech.com hosts a standard primary zone for the publitech.com domain. You recently delegated a subdomain named portland.publitech.com to the Portland branch office and a subdomain named santafe.publitech.com to the Santa Fe branch office. At each branch office, the local administrator installed and configured a Windows 2000 Server computer as a DNS server. The following exhibit illustrates the DNS domain namespace of PubliTech's network:
Users in the publitech.com and santafe.publitech.com domains report that they cannot access any resources in the portland.publitech.com domain by specifying host names. You use the Nslookup utility to query ns.publitech.com, and, based on the results, you know that the following resource records exist in the publitech.com DNS zone file on ns.publitech.com:
What resource record should you modify in order to enable users in the publitech.com and santafe.publitech.com domains to access resources in the portland.publitech.com domain?
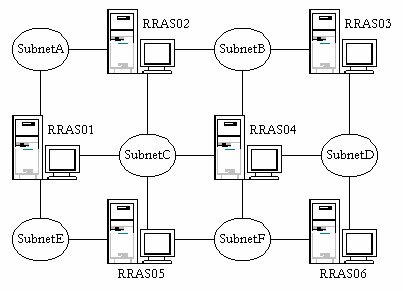
4. You are the network administrator for your company. The network for your company is configured as shown in the exhibit.
You configure Windows 2000 Server computers with the Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) to serve as the routers for your network. You need to configure the RRAS computers to enable routing between the subnets. You want to minimize the amount of administrative effort involved in maintaining the routers. Additionally, you want to minimize the amount of convergence time for the routers, and you want to minimize the amount of traffic that is generated by routing table updates. Which of the following actions should you take to configure the RRAS computers to meet your objectives?
5. Your network consists of 120 Windows 2000 Professional computers, 10 Windows 2000 Server computers, 3 NetWare 3.11 servers and 2 NetWare 4.1 servers on a single Ethernet segment. The Windows 2000 Server computers use Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) as their only networking protocol. The network IP address is 192.168.99.0/24 and there is no DHCP or BOOTP server on the network. The NetWare servers use only Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange (IPX/SPX) and each NetWare server uses only the default Ethernet frame type. The Windows 2000 Professional computers must be able to access resources on the Windows 2000 Server computers, NetWare 3.11 servers and NetWare 4.1 servers. Which of the following should you do to configure a Windows 2000 Professional computer to access all of the Windows 2000 Server computers, NetWare 3.11 servers and NetWare 4.1 servers on this network?
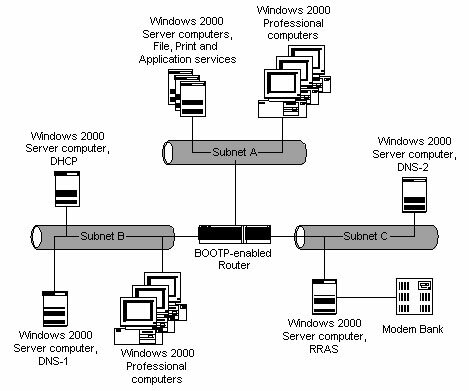
6. Your network contains two LANs that are connected by a BOOTP-enabled router. Subnet A consists of 200 Windows 2000 Professional computers and several Windows 2000 Server computers that provide application, file and print services for your network. Subnet B consists of 1,000 Windows 2000 Professional clients, a DHCP server and a DNS server named DNS-1, which is used by all computers on the network. To enable remote access, you have installed a second DNS server, which is named DNS-2, and a Windows 2000 Server computer with the Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) on a new segment, Subnet C. The exhibit illustrates the new layout of the network.
The RRAS server uses DNS-1 for name resolution. You want remote clients to use DNS-2 for name resolution. Which of the following steps should you take to ensure that remote clients are configured to use DNS-2 for name resolution?
Answers: 1) Choice b is correct. By default, a NAT server allows outbound traffic to the Internet but only allows inbound traffic if it is return traffic through a connection that was established by an internal host. To allow Internet hosts to access your Web site in this scenario, you should create a special port that maps the public IP address and port number of the NAT server to the private IP address and port number of the Web server. You should use a special port to accomplish this only if the public interface of the NAT server is configured with a single public IP address. When the public interface of the NAT server is configured with multiple IP addresses, you should use address reservations to map specific external addresses to specific internal addresses. To create a special port, access the Special Ports tab of the Properties sheet for the public interface in the Routing and Remote Access console, select the TCP protocol or the UDP protocol and click the Add button. In the Add Special Port dialog box, select the On this interface option, and specify the incoming TCP or UDP port on the NAT server to which Internet hosts will connect. Then, specify the Web server's IP address and the Web server's outgoing TCP or UDP port to which the NAT server will forward packets. You can use IP filters on the private and public interfaces of the NAT server in order to restrict access to the private network and to the Internet, respectively. However, you cannot use IP filters to enable Internet hosts to access your Web site. If no DNS server is present on the internal network, then you can configure name resolution on the private interface of the NAT server to cause the NAT server to forward internal network name resolution queries to Internet DNS servers. Configuring name resolution will not enable Internet hosts to access your Web site. Reference: W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "Routing and Remote Access," "Routing," "Concepts," "Using Routing," "Deploying Routing," "Setting Up Network Address Translation," "Network address translation design considerations." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "Routing and Remote Access," "Routing," "Concepts," "Understanding Routing," "Understanding Network Address Translation." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "Routing and Remote Access," "Routing," "How To...," "Configure Network Address Translation," "Configure interface special ports." 2) Choice b is correct. To minimize costs and still allow each office to fully manage its own DNS database and have the ability to create subdomains of their own namespace, you should register a single domain name, delegate a subdomain to each location and install a DNS server at each location. To minimize costs, you should register a single domain name, such as metroil.com, rather than one domain name for each location; with a delegated subdomain, such as nashville.metroil.com, each location can maintain their own DNS database and create subdomains just as they would with their own second-level domain name. Although installing a single DNS server would minimize costs, it would do so at the expense of your goal of allowing each office to fully manage its own DNS database. To allow each office to fully manage its own DNS database, you should install a DNS server at each location. Reference: W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "Concepts," "Using DNS," "Managing zones," "Delegating zones." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "Concepts," "Using DNS," "Planning issues," "Namespace planning for DNS." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "Concepts," "Using DNS," "Planning issues," "Server planning for DNS." www.microsoft.com/TechNet/winnt/Winntas/technote/ruley/ch07.asp TechNet, Contents, "Windows Product Family," "MS Windows NT," "MS Windows NT Server," "Technical Notes," "Networking Windows NT 4.0," "Chapter 7 Internet Connections." www.microsoft.com/TechNet/winnt/Winntas/technote/ruley/ch07.asp TechNet, Contents, "Windows Product Family," "MS Windows NT," "MS Windows NT Server," "Technical Notes," "Networking Windows NT 4.0," "Chapter 7 Internet Connections." 3) Choice c is correct. Name server (NS) resource records are used to indicate which DNS servers are authoritative for which domains. The following is the correct syntax for an NS resource record: delegated_subdomain_name [ttl] IN NS name_server You should delete the portland.publitech.com. IN NS ns.portland.publitech.com record and create the portland.publitech.com. IN NS dns.portland.publitech.com NS record in order to enable users in the publitech.com and santafe.publitech.com domains to access resources in the portland.publitech.com domain. The NS record displayed in the scenario indicates that the name of the DNS server that hosts the portland.publitech.com primary zone is named ns.portland.publitech.com, but the exhibit shows that the Portland branch administrator named the DNS server dns.portland.publitech.com. Users in the publitech.com and santafe.publitech.com domains are unable to use host names to access resources in the portland.publitech.com domain because DNS queries for that domain are not being directed to the correct DNS server. All other resource records shown are correct in this scenario. Address (A), or host, resource records are used to map host names to IP addresses. The following is the correct syntax for an A (host) resource record: host_name [ttl] IN A IP_address. Reference: W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "Concepts," "Using DNS," "Managing zones," "Managing authority records." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "Concepts," "Resources," "Resource records reference." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "Concepts," "Using DNS," "Planning issues," "Namespace planning for DNS." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "Concepts," "Using DNS," "Managing zones," "Delegating zones." W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "DNS," "How To...," "Troubleshoot DNS Using Command Tools," "Verify a zone delegation using the nslookup command." 4) Choice d is correct. You should configure the RRAS computers on your network with the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. OSPF provides several advantages over Routing Information Protocol version 1 (RIP v1) and version 2 (RIP v2). OSPF requires very little network overhead. As changes are made to the network topology, the changes are propagated to the rest of the network immediately, thus reducing convergence time. As the network grows, you can create OSPF areas to divide the network. When you configure an OSPF area, the routers contained within a particular area only contain routing information for that area; the routing table on an RRAS computer within an area does not have to contain routing information for the entire network. An OSPF area is connected to other divisions of the network through an area border router that contains routing information for the other networks. OSPF routers maintain network information in a link state database. The link state database is essentially a map of the internetwork. Although the administrative effort required to maintain OSPF routers is minimized after installation, configuration of an OSPF router is more complex than RIP for IP. RIP v1 and RIP v2 are distance-vector routing protocols; RIP v1 and RIP v2 routers periodically broadcast the routes that are contained on the routing table to the network. However, the changes are not broadcast immediately. If a router configured with RIP v1 or v2 were not functioning, then the router could not notify the other routers in the network that it was down. Because a route contained on a RIP router has a maximum lifetime of three minutes, a maximum of three minutes is allowed for convergence of a network to be completed if another router on the network goes down. Configuring all of the RRAS computers with static routes would not meet your objective of minimizing administrative effort; you would have to manually update each router in a statically routed network as changes occur on the network. Reference: W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "Routing and Remote Access," "Routing," "Concepts," "Understanding Routing," "Understanding Unicast Routing," "IP Routing Protocols," "OSPF." W2KSRK, Contents, "Internetworking Guide," "Routing," "Unicast IP Routing," "RIP for IP," "RIP for IP Operation." 5) Only choices a, b, e and g are correct. To configure a Windows 2000 Professional computer to access all of the Windows 2000 Server computers, NetWare 3.11 servers and NetWare 4.1 servers on this network, you should install the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), install the NWLink IPX/SPX/NetBIOS Compatible Transport Protocol, manually configure the computer with an IP address and manually configure the 802.2 and 802.3 frame types in the Registry. Because the Windows 2000 Server computers use TCP/IP exclusively, you should install the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) on the Windows 2000 Professional computer in order for it to access the Windows 2000 Server computers. Because there is no DHCP or BOOTP server on the network and the network IP address is 192.168.99.0/24, you should manually configure the IP address of the Windows 2000 Professional computer. If there had been a DHCP or BOOTP server on the network or if the network IP address had been the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) network address 169.254.0.0/16, then you should have configured the Windows 2000 Professional computer to Obtain an IP address automatically. Because the NetWare servers use IPX/SPX exclusively, you should install the NWLink IPX/SPX/NetBIOS Compatible Transport Protocol on the Windows 2000 Professional computer in order for it to access the NetWare servers. Because the NetWare servers are a mix of version 3.11 and version 4.1 and each uses only the default Ethernet frame type, you should manually configure the 802.2 and 802.3 frame types in the Registry. NetWare versions 3.11 and earlier use 802.3 as the default Ethernet frame type, whereas NetWare 3.12 and higher use 802.2 as the default Ethernet frame type. For a client computer to connect to a server by using IPX/SPX, both the client computer and the server must share a common frame type. If a Windows 2000 computer is configured to automatically detect frame type and multiple frame types are present on the network, then the Windows 2000 computer will use only the 802.2 frame type. Windows 2000 Professional computers and Windows 2000 Server computers can be manually configured to use multiple Ethernet frame types. Although Windows 2000 Server computers can be manually configured to use multiple frame types by using the Properties sheet for the appropriate connection, the Registry must be altered to manually configure Windows 2000 Professional computers to use multiple frame types. The AppleTalk Protocol would be installed to allow the computer to communicate with Macintosh computers and other computers running the AppleTalk protocol. Reference: W2KPOH, Search, "Configure NWLink." W2KSOH, Contents, "Network Interoperability," "Novell NetWare Integration," "Best Practices," "Best practices for NWLink." support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/Q150/5/46.asp TechNet, Contents, "Knowledge Base," "MS Windows NT Current Release," "NWLink IPX/SPX: Network Number vs. Internal Network Number." 6) Only choices b, d and f are correct. To ensure that remote clients are configured to use DNS-2 for name resolution, you should configure the RRAS server to provide remote clients with addresses obtained from the DHCP server, create a scope for Subnet C on the DHCP server, add the assignment for DNS-2 to the new scope and install the DHCP Relay Agent on the RRAS server. For any computer on Subnet C to obtain leases from the DHCP server, you must create a scope for Subnet C and configure the scope with the options desired. If, as in this case, you want the DHCP clients on Subnet C to use DNS-2, then the scope should include the assignment to use DNS-2. To ensure that the remote clients receive addresses that are assigned by the DHCP server, the RRAS server must be configured to use DHCP-assigned addresses when configuring clients. To ensure that the remote access clients receive the DNS option that is assigned by the DHCP server, the DHCP Relay Agent must be installed on the RRAS server; if no DHCP Relay Agent is installed on the RRAS server, then clients will use the same DNS server that the RRAS server uses, which, in this scenario, is DNS-1. If the RRAS server is configured to assign IP addresses from a static pool, then remote clients that connect to the RRAS server will use the same DNS and WINS server addresses that have been assigned to the RRAS server. The static address pool cannot be configured with the DNS-2 assignment directly; if you want the remote access clients to receive IP addresses from a static address pool and use DNS-2, then the RRAS server must be configured to use DNS-2. Because a BOOTP-enabled router is already in use, the RRAS server is able to obtain IP leases from the DHCP server on Subnet B if it is configured to do so; there is no need to add a DHCP relay agent on the router interface that is attached to Subnet C. Reference: W2KSOH, Contents, "Networking," "Routing and Remote Access," "Remote Access," "Concepts," "Understanding remote access," "LAN protocols," "TCP/IP and remote access." W2KSRK, Contents, "Internetworking Guide," "Remote Access," "Remote Access Server," "Remote Access and TCP/IP and IPX," "TCP/IP." W2KSRK, Contents, "TCP/IP Core Networking Guide," "Address Allocation and Name Resolution," "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol," "Managing DHCP Options," "DHCP Option Parameters." These questions and answers are provided by Transcender LLC. Order the full version of this exam simulation online at www.transcender.com, phone 615-726-8779, 8 a.m. - 6 p.m., (CST), M - F, fax 615-726-8884, or mail to Transcender LLC, 565 Marriott Drive, Suite 300, Nashville, TN 37214. More Pop Quiz: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
top Copyright 2000-2009, 101communications LLC. See our Privacy Policy. For more information, e-mail . |